Розробка компактних черенковських приладів зі стрічковими електронними пучками субТГц і ТГц діапазонів частот (огляд)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.20535/S002134702403004XКлючові слова:
електронно-хвильова взаємодія, клинотрон, лампа зворотної хвилі, лампа біжучої хвилі, Черенковський електровакуумний прилад, сповільнююча система, бі-періодична решітка, надгабаритний хвилевід, T-перехід, S-матриця, перетворення мод, гібридна об’ємна поверхнева мода, витікаюча хвиля, випромінювання Сміта-Перселла, поверхневий плазмон-поляритон, ТГц випромінюванняАнотація
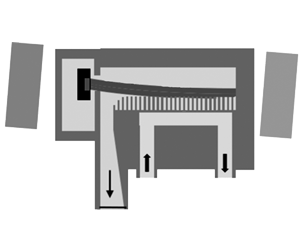
В роботі представлено та проведено обговорення результатів теоретичних та експериментальних досліджень процесів електронно-хвильової взаємодії в компактних вакуумних електронних приладах типу клинотрона. Запропоновано декілька модифікацій простору взаємодії приладів та виводу енергії випромінювання для поліпшення характеристик клинотронів субТГц і ТГц діапазонів частот. Зокрема, проведено оптимізацію традиційної конструкції клинотрона для покращення електронно-хвильової взаємодії та забезпечення одномодового вихідного випромінювання в надрозмірній електродинамічній системі приладів. Крім того, розглянуто новий підхід до проєктування черенковських генераторів і підсилювачів ТГц діапазону, який ґрунтується на збудженні гібридних об’ємно-поверхневих мод у електродинамічних системах приладів, що містять багатоперіодичні гребінки. Теоретичні дослідження проводилися з використанням як «холодного» так і «гарячого» моделювання за допомогою розробленого власного та комерційного програмного забезпечення. Представлено типові характеристики експериментальних приладів, що працюють у діапазоні частот від 90 до 410 ГГц. Проведено їх порівняння з результатами теоретичних розрахунків. Також окреслено плани подальших досліджень і розробок ТГц приладів.
Посилання
- A. Leitenstorfer et al., “The 2023 terahertz science and technology roadmap,” J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., vol. 56, no. 22, p. 223001, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/acbe4c.
- X. Chen et al., “Terahertz (THz) biophotonics technology: Instrumentation, techniques, and biomedical applications,” Chem. Phys. Rev., vol. 3, no. 1, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0068979.
- X. Ding, A. I. Hernandez-Serrano, J. J. Young, E. Pickwell-MacPherson, “Variation of skin hydration profile with biophysical factors and lifestyle revealed by in vivo terahertz sensing,” Biomed. Opt. Express, vol. 15, no. 9, p. 5180, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1364/BOE.527731.
- C. M. Armstrong et al., “Frontiers in the application of RF vacuum electronics,” IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. 70, no. 6, pp. 2643–2655, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2023.3239841.
- M. Blank, K. L. Felch, “Millimeter-wave sources for DNP-NMR,” eMagRes, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 155–166, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470034590.emrstm1582.
- M. Thumm, “State-of-the-art of high-power gyro-devices and free electron masers,” J. Infrared, Millimeter, Terahertz Waves, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 1–140, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-019-00631-y.
- S. Sabchevski, M. Glyavin, S. Mitsudo, Y. Tatematsu, T. Idehara, “Novel and emerging applications of the gyrotrons worldwide: current status and prospects,” J. Infrared, Millimeter, Terahertz Waves, vol. 42, no. 7, pp. 715–741, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-021-00804-8.
- T. Idehara, S. P. Sabchevski, M. Glyavin, S. Mitsudo, “The gyrotrons as promising radiation sources for THz sensing and imaging,” Appl. Sci., vol. 10, no. 3, p. 980, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030980.
- G. A. Komandin et al., “BWO generators for terahertz dielectric measurements,” IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol., vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 440–444, 2013, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TTHZ.2013.2255914.
- Г. Я. Левин, А. И. Бородкин, А. Я. Кириченко, А. Я. Усиков, С. А. Чурилова, Клинотрон. Киев: Наукова думка, 1992.
- A. Likhachev et al., “Compact radiation module for THz spectroscopy using 300 GHz continuous-wave clinotron,” Rev. Sci. Instruments, vol. 90, no. 3, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5064796.
- В. П. Шестопалов, Ed., Генераторы Дифракционного Излучения. Киев: Наукова думка, 1991.
- V. L. Bratman, B. S. Dumesh, A. E. Fedotov, P. B. Makhalov, B. Z. Movshevich, F. S. Rusin, “Terahertz orotrons and oromultipliers,” IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., vol. 38, no. 6, pp. 1466–1471, 2010, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPS.2010.2041367.
- K. Lukin, E. Khutoryan, A. Kuleshov, S. Ponomarenko, M. Sattorov, G.-S. Park, “THz oscillators based on Cherenkov, Smith-Purcell and hybrid radiation effects,” in Advances in Terahertz Source Technologies, New York: Jenny Stanford Publishing, 2024, pp. 487–523.
- S. S. Ponomarenko et al., “Spectral characteristics of THz CW clinotrons,” IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. 67, no. 12, pp. 5766–5770, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2020.3032940.
- A. F. Krupnov, “Phase lock-in of MM/SUBMM backward wave oscillators: development, evolution, and applications,” Int. J. Infrared Millim. Waves, vol. 22, pp. 1–18, 2001, doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010744901186.
- E. M. Khutoryan et al., “Simultaneous stabilization of gyrotron frequency and power by PID double feedback control on the acceleration and anode voltages,” J. Infrared, Millimeter, Terahertz Waves, vol. 38, no. 7, pp. 813–823, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-017-0374-1.
- A. Likhachev et al., “Supply voltage control for guaranteed performance of compact terahertz vacuum electron devices,” Rev. Sci. Instruments, vol. 92, no. 12, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0070533.
- E. N. Odarenko, A. A. Shmal’ko, “Nonlinear theory of O-type microwave oscillators with nonuniform dc magnetic field (2-D model),” Radiotekhnika i Elektron., vol. 39, no. 4, pp. 653–661, 1994.
- “Магнитная фокусирующая система интенсивных электронных пучков для клинотронов субмиллиметрового диапазона,” Appl. nonlinear Dyn. Izv. VUZ, vol. 20, no. 5, 2012, doi: https://doi.org/10.18500/0869-6632-2012-20-5-112-120.
- S. S. Ponomarenko et al., “400-GHz continuous-wave clinotron oscillator,” IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 82–86, 2013, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPS.2012.2226247.
- K. Schunemann, D. M. Vavriv, “Theory of the clinotron: A grating backward-wave oscillator with inclined electron beam,” IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. 46, no. 11, pp. 2245–2252, 1999, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/16.796302.
- V. S. Andrushkevich, Y. G. Gamayunov, E. V. Patrusheva, “A nonlinear clinotron theory,” J. Commun. Technol. Electron., vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 330–336, 2010, doi: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064226910030125.
- S. Vlasenko et al., “Radiation output of the 330 GHz continuous-wave clinotron oscillator with modified cavity,” IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. 71, no. 6, pp. 3940–3944, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2024.3394796.
- Y. S. Kovshov et al., “Effect of mode transformation in THz clinotron,” J. Infrared, Millimeter, Terahertz Waves, vol. 39, no. 11, pp. 1055–1064, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-018-0534-y.
- S. O. Steshenko, “Generalization of the mode-matching technique to the problems of scattering by semi-infinite slow-wave structures,” Radiophys. Electron., vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 10–17, 2020, uri: http://jnas.nbuv.gov.ua/uk/article/UJRN-0001183349.
- E. Khutoryan, A. Kuleshov, S. Ponomarenko, K. Lukin, Y. Tatematsu, M. Tani, “Efficient excitation of hybrid modes in a THz clinotron,” J. Infrared, Millimeter, Terahertz Waves, vol. 42, no. 6, pp. 671–683, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-021-00800-y.
- E. M. Khutoryan, A. N. Kuleshov, S. S. Ponomarenko, K. A. Lukin, Y. Tatematsu, M. Tani, “Hybrid bulk-surface modes excited by a sheet electron beam in THz Cherenkov oscillator,” IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. 69, no. 6, pp. 3407–3412, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2022.3168526.
- J. Feng et al., “Fabrication of a 0.346-THz BWO for plasma diagnostics,” IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. 65, no. 6, pp. 2156–2163, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2018.2821683.
- A. Srivastava, S. Penmetsa, L. Christie, K. N. Bhat, “Electromagnetic design of a 220 GHz BWO with experimental study of micro-fabricated folded waveguide structure,” J. Electromagn. Waves Appl., vol. 33, no. 14, pp. 1860–1873, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/09205071.2019.1645744.
- C. Paoloni, D. Gamzina, R. Letizia, Y. Zheng, N. C. Luhmann, “Millimeter wave traveling wave tubes for the 21st century,” J. Electromagn. Waves Appl., vol. 35, no. 5, pp. 567–603, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/09205071.2020.1848643.
- D. M. Vavriv, “Theory of the clinotron,” Telecommun. Radio Eng., vol. 67, no. 9, pp. 757–781, 2008, doi: https://doi.org/10.1615/TelecomRadEng.v67.i9.10.
- C. Y. Levin, A. Y. Kirichenko, A. I. Borodkin, S. A. Churilova, A. Y. Usikov, “The clinotron,” in 22nd European Microwave Conference, 1992, 1992, pp. 603–607, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/EUMA.1992.335771.
- B. P. Yefimov, M. V. Milcho, “O-type millimeter-wave band generator of amplitude-modulated oscillations with resonance interaction space,” Int. J. Infrared Millim. Waves, vol. 18, no. 9, pp. 1681–1687, 1997, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02678279.
- S. Ponomarenko et al., “Operational characteristics of the 175-GHz continuous-wave clinotron,” IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. 70, no. 11, pp. 5921–5925, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2023.3316157.
- V. D. Yeryomka, O. F. Pishko, “Klynotronic effect in vacuum sources of terahertz electromagnetic oscillations,” Telecommun. Radio Eng., vol. 78, no. 18, pp. 1601–1636, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1615/TelecomRadEng.v78.i18.10.
- M. V. Mil’cho, I. V. Lopatin, V. V. Zavertanny, A. S. Tishchenko, K. Ilyenko, “CW clinotrons for the short-wave part of the millimeter waveband,” in IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference, 2014, pp. 71–72, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IVEC.2014.6857495.
- Y. S. Kovshov, S. S. Ponomarenko, S. A. Kishko, E. M. Khutoryan, A. N. Kuleshov, “Numerical simulation and experimental study of sub-THz and THz CW clinotron oscillators,” IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. 65, no. 6, pp. 2177–2182, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2018.2792258.
- A. A. Likhachev et al., “Effect of electron beam velocity spread in a clinotron,” IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. 66, no. 3, pp. 1540–1544, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2019.2891547.
- “Poisson Superfish 7.1,” Software. https://poisson-superfish.software.informer.com/7.1/.
- CST, “GPU Computing Guide,” CST Studio Suite R2022, 2021.
- Y. S. Kovshov et al., “High frequency ohmic losses in terahertz frequency range CW klynotrons,” Telecommun. Radio Eng., vol. 76, no. 10, pp. 929–940, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1615/TelecomRadEng.v76.i10.90.
- Е. Е. Лысенко, О. Ф. Пишко, В. Г. Чумак, С. А. Чурилова, “Добротность резонансной линии клинотронов миллиметрового диапазона,” Радиофизика и радиоастрономия, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 317–322, 2001, uri: http://dspace.nbuv.gov.ua/handle/123456789/122283.
- E. M. Khutoryan et al., “Excitation of hybrid space-surface waves in clinotrons with non-uniform grating,” J. Infrared, Millimeter, Terahertz Waves, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 236–249, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-017-0453-3.
- T. López-Rios, D. Mendoza, F. J. García-Vidal, J. Sánchez-Dehesa, B. Pannetier, “Surface shape resonances in lamellar metallic gratings,” Phys. Rev. Lett., vol. 81, no. 3, pp. 665–668, 1998, doi: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.665.
- A. T. ATK, MAGIC 3.2.0 Help Manual. Newington, VA, USA: Alliant Techsystems ATK, 2011.
- V. Petrov, J. Kokkoniemi, D. Moltchanov, J. Lehtomaki, Y. Koucheryavy, M. Juntti, “Last meter indoor terahertz wireless access: performance insights and implementation roadmap,” IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 56, no. 6, pp. 158–165, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2018.1600300.
- P. Rodriguez-Vazquez, J. Grzyb, B. Heinemann, U. R. Pfeiffer, “A 16-QAM 100-Gb/s 1-M wireless link with an EVM of 17% at 230 GHz in an SiGe technology,” IEEE Microw. Wirel. Components Lett., vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 297–299, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/LMWC.2019.2899487.
- Y. Zheng, S. Qiu, B. Griffin, R. Kowalczyk, N. C. Luhmann, D. Gamzina, “Compact E-band sheet beam folded waveguide traveling wave tube for high data rate communication,” IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. 70, no. 5, pp. 2508–2513, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2023.3252494.
- S. S. Ponomarenko et al., “Traveling-wave amplification in a circuit with nonuniform grating,” IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. 68, no. 10, pp. 5232–5237, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2021.3105951.
- V. P. Taranenko, A. A. Mikhin, “Investigation of methods for the suppression of self-oscillation in O-type traveling-wave tubes,” Izv. Vyss. Uchebnykh Zaved. Radioelektronika, vol. 17, no. 11, pp. 5–17, 1974.
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2024 Вісті вищих учбових закладів. РадіоелектронікаИздатель журнала Известия высших учебных заведений. Радиоэлектроника (сокр. "Известия вузов. Радиоэлектроника"), Национальный технический университет Украины "Киевский политехнический институт", учитывает, что доступ автора к его статье является важным как для самого автора, так и для спонсоров его исследований. Мы представлены в базе издателей SHERPA/RoMEO как зеленый издатель (green publisher), что позволяет автору выполнять самоархивирование своей статьи. Однако важно, чтобы каждая из сторон четко понимала свои права. Просьба более детально ознакомиться с Политикой самоархивирования нашего журнала.
Политика оплаченного открытого доступа POA (paid open access), принятая в журнале, позволяет автору выполнить все необходимые требования по открытому доступу к своей статье, которые выдвигаются институтом, правительством или фондом при выделении финансирования. Просьба более детально ознакомиться с политикой оплаченного открытого доступа нашего журнала (см. отдельно).
Варианты доступа к статье:
1. Статья в открытом доступе POA (paid open access)
В этом случае права автора определяются лицензией CC BY (Creative Commons Attribution).
2. Статья с последующим доступом по подписке
В этом случае права автора определяются авторским договором, приведенным далее.
- Автор (каждый соавтор) уступает Издателю журнала «Известия высших учебных заведений. Радиоэлектроника» НТУУ «КПИ» на срок действия авторского права эксклюзивные права на материалы статьи, в том числе право на публикацию данной статьи издательством Аллертон Пресс, США (Allerton Press) на английском языке в журнале «Radioelectronics and Communications Systems». Передача авторского права охватывает исключительное право на воспроизведение и распространение статьи, включая оттиски, переводы, фото воспроизведения, микроформы, электронные формы (он- и оффлайн), или любые иные подобные формы воспроизведения, а также право издателя на сублицензирование третьим лицам по своему усмотрению без дополнительных консультаций с автором. При этом журнал придерживается Политики конфиденциальности.
- Передача прав включает право на обработку формы представления материалов с помощью компьютерных программам и систем (баз данных) для их использования и воспроизводства, публикации и распространения в электронном формате и внедрения в системы поиска (базы данных).
- Воспроизведение, размещение, передача или иное распространение или использование материалов, содержащихся в статье должно сопровождаться ссылкой на Журнал и упоминанием Издателя, а именно: название статьи, имя автора (соавторов), название журнала, номер тома, номер выпуска, копирайт авторов и издателя "© Национальный технический университет Украины "Киевский политехнический институт"; © автор(ы)".
- Автор (каждый соавтор) материалов сохраняет все права собственника материалов, включая патентные права на любые процессы, способы или методы и др., а также права на товарные знаки.
- Издатель разрешает автору (каждому соавтору) материалов следующее:
- Право пользоваться печатными или электронными вариантами материалов статьи в форме и содержании, принятыми Издателем для публикации в Журнале. Подробнее см. политики Оплаченного открытого доступа, подписки и самоархивирования.
- Право бесплатно копировать или передавать коллегам копию напечатанной статьи целиком или частично для их личного или профессионального использования, для продвижения академических или научных исследований или для учебного процесса или других информационных целей, не связанных с коммерческими целями.
- Право использовать материалы из опубликованной статьи в написанной автором (соавторами) книге, монографии, учебнике, учебном пособии и других научных и научно-популярных изданиях.
- Право использовать отдельные рисунки или таблицы и отрывки текста из материалов в собственных целях обучения или для включения их в другую работу, которая печатается (в печатном или электронном формате) третьей стороной, или для представления в электронном формате во внутренние компьютерные сети или на внешние сайты автора (соавторов).
- Автор (соавторы) соглашаются, что каждая копия материалов или любая ее часть, распространенная или размещенная ими в печатном или электронном формате, будет содержать указание на авторское право, предусмотренное в Журнале и полную ссылку на Журнал Издателя.
- Автор (соавторы) гарантирует, что материалы являются оригинальной работой и представлены впервые на рассмотрение только в этом Журнале и ранее не публиковались. Если материалы написаны совместно с соавторами, автор гарантирует, что проинформировал их относительно условий публикации материалов и получил их подписи или письменное разрешение подписываться от их имени.
- Если в материалы включаются отрывки из работ или имеются указания на работы, которые охраняются авторским правом и принадлежат третьей стороне, то автору необходимо получить разрешение владельца авторских прав на использование таких материалов в первом случае и сделать ссылку на первоисточник во втором.
- Автор гарантирует, что материалы не содержат клеветнических высказываний и не посягают на права (включая без ограничений авторское право, права на патент или торговую марку) других лиц и не содержат материалы или инструкции, которые могут причинить вред или ущерб третьим лицам. Автор (каждый соавтор) гарантирует, что их публикация не приведет к разглашению секретных или конфиденциальных сведений (включая государственную тайну). Подтверждением этого является Экспертное заключение (см. перечень документов в Правила для авторов).
- Издатель обязуется опубликовать материалы в случае получения статьей положительного решения редколлегии о публикации на основании внешнего рецензирования (см. Политика рецензирования).
- В случае публикации статьи на английском языке в журнале «Radioelectronics and Communications Systems» (Издатель: Аллертон Пресс, США, распространитель Springer) автору (соавторам) выплачивается гонорар после выхода последнего номера журнала года, в котором опубликована данная статья.
- Документ Согласие на публикацию, который подают русскоязычные авторы при подаче статьи в редакцию, является краткой формой данного договора, в котором изложены все ключевые моменты настоящего договора и наличие которого подтверждает согласие автора (соавторов) с ним. Аналогичным документом для англоязычных авторов является Copyright Transfer Agreement (CTA), предоставляемый издательством Allerton Press.
- Настоящий Договор вступает в силу в момент принятия статьи к публикации. Если материалы не принимаются к публикации или до публикации в журнале автор (авторы) отозвал работу, настоящий Договор не приобретает (теряет) силу.



